The Topic Which is Covered in This Article
Variable
Variable name convention Rules
Hoisting
Variable Scope
- variable scope
- block scope
- global scope
Datatypes in Javascript
What Is NaN?
Type Of Operators
Difference With Null vs Undefined
Expression And Operators
1 Assignment operators
2 Arithmetic operators
3Logical operators
4 Comparison operators
5 String Concatenation(operators)
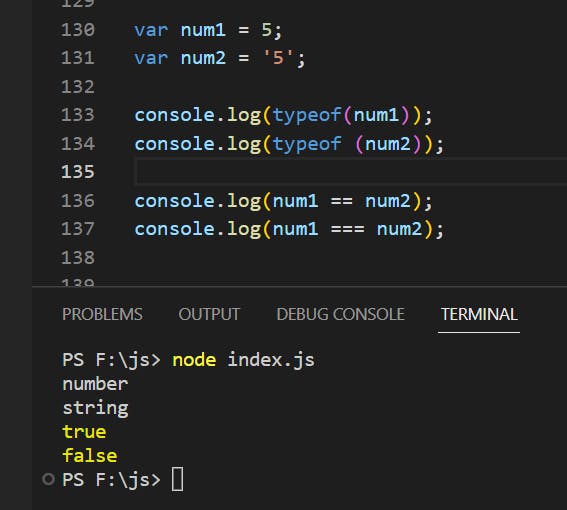
What Is the Difference between == vs ===?
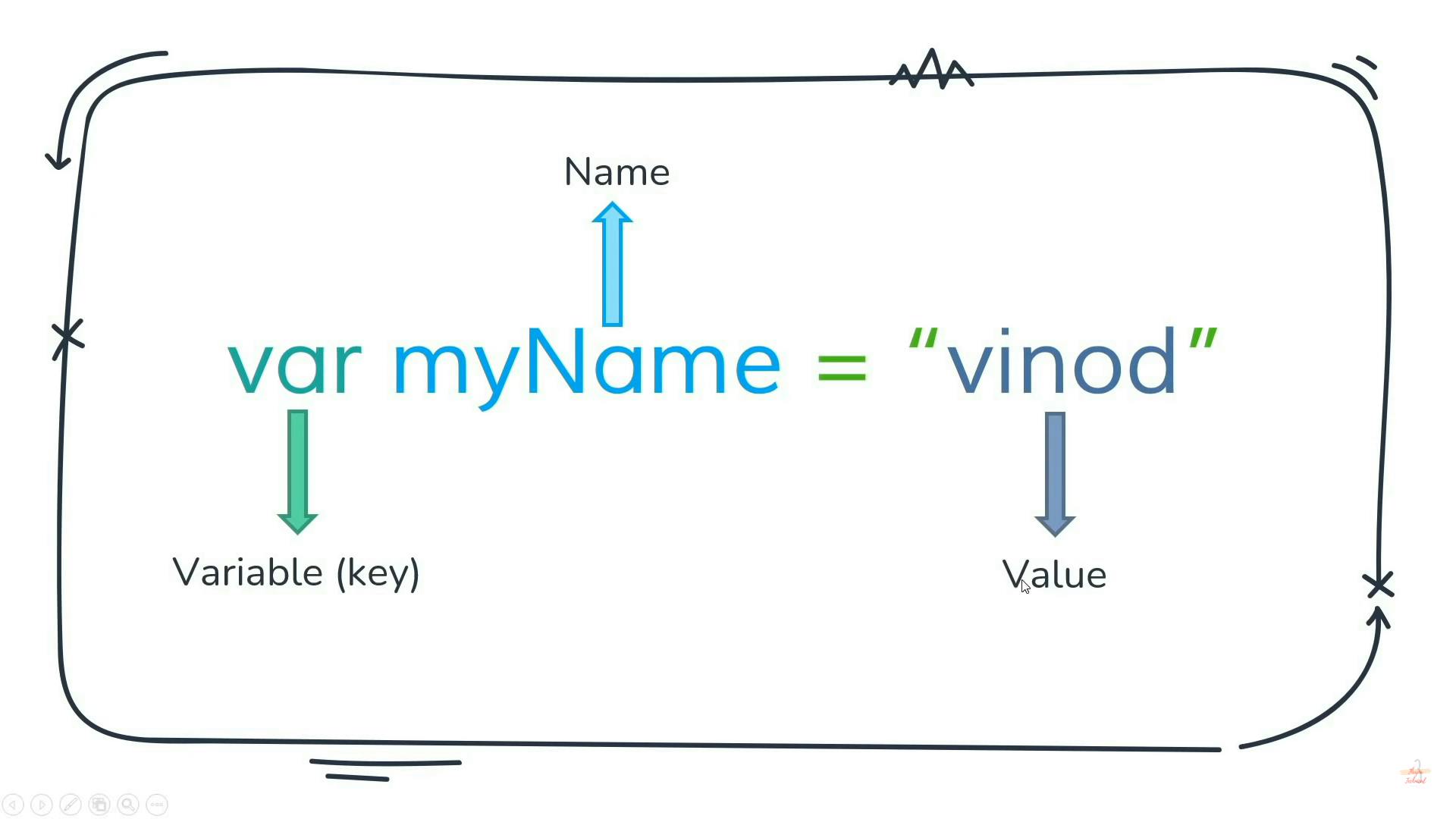
Variable
📌Variable declaration
🪢 var
🪢let
🪢const
📌Hoisting
📌Variable Naming Rules
📌Variable Scopes
🪢Block
🪢Function
🪢Global
javascript improves the user experience of the web page by converting it from a static page into an interactive one or javascript adds behaviour to web pages
📌Variable declaration
📌There are 3 Types of Javascript Variable
➡️Variable simply store value
🪢var
🪢let
🪢const
📌Let
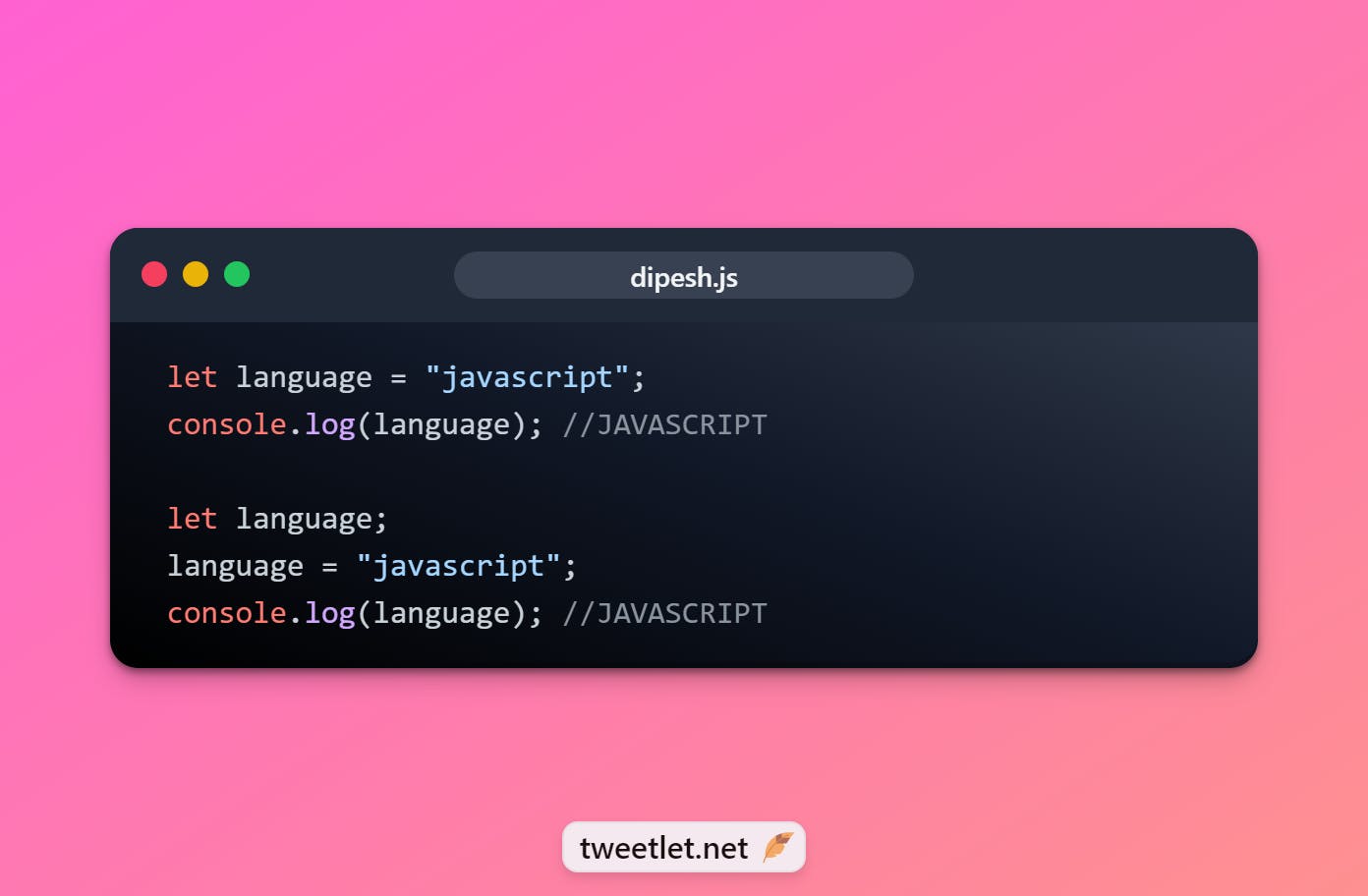
let language = "javascript"; console.log(language); //JAVASCRIPT let language; language = "javascript"; console.log(language); //JAVASCRIPT
📌const
➡️once declare cant change
➡️its good because in a real application mutations less (change in value) then also bug will less
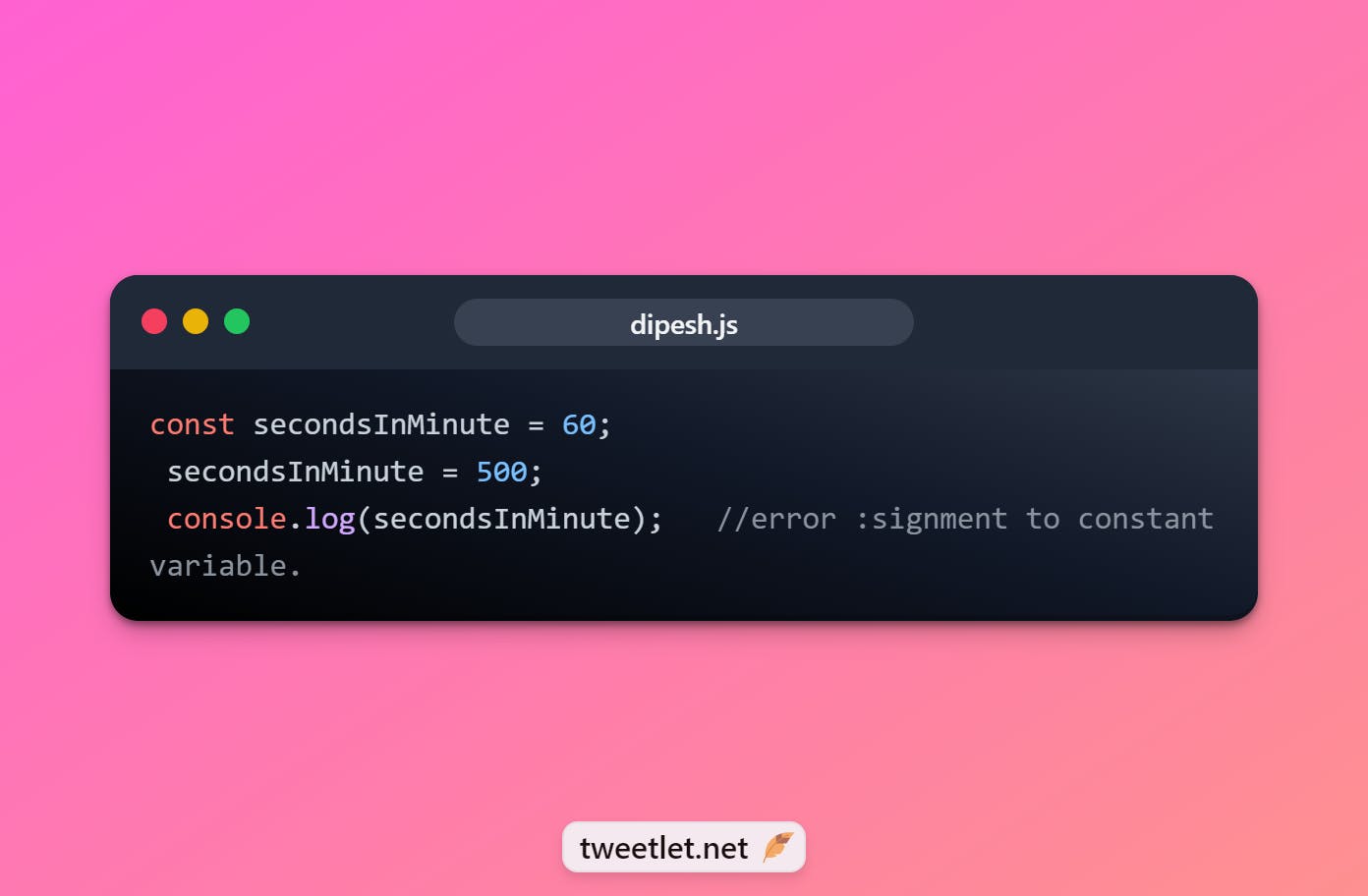
const secondsInMinute = 60; secondsInMinute = 500; console.log(secondsInMinute); //error :signment to constant variable.📌Variable name convention Rules
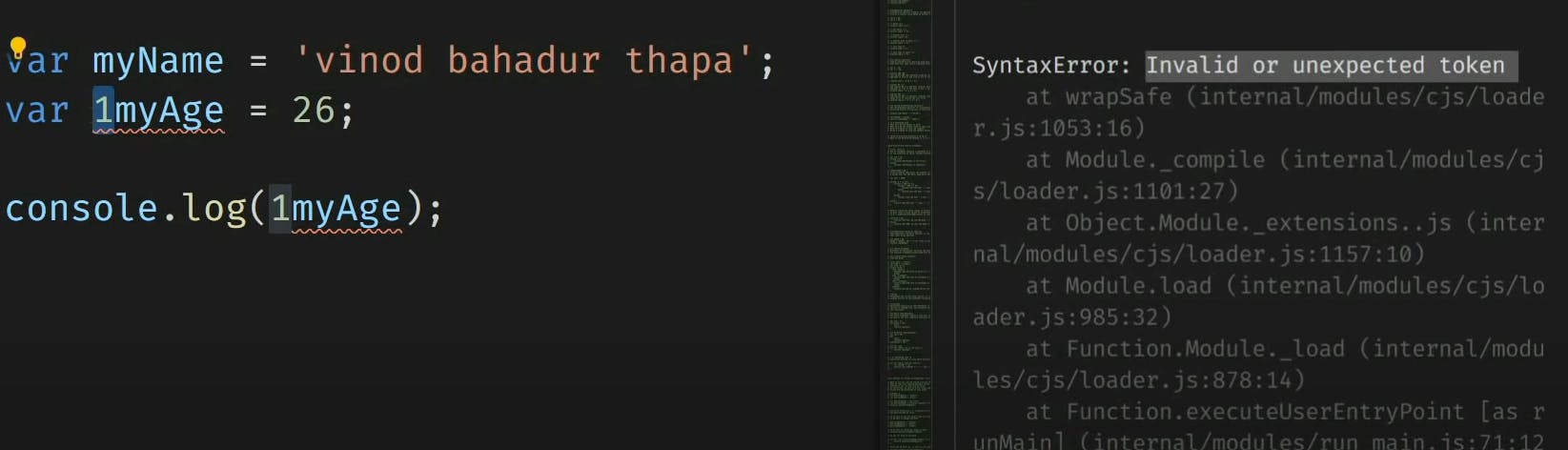
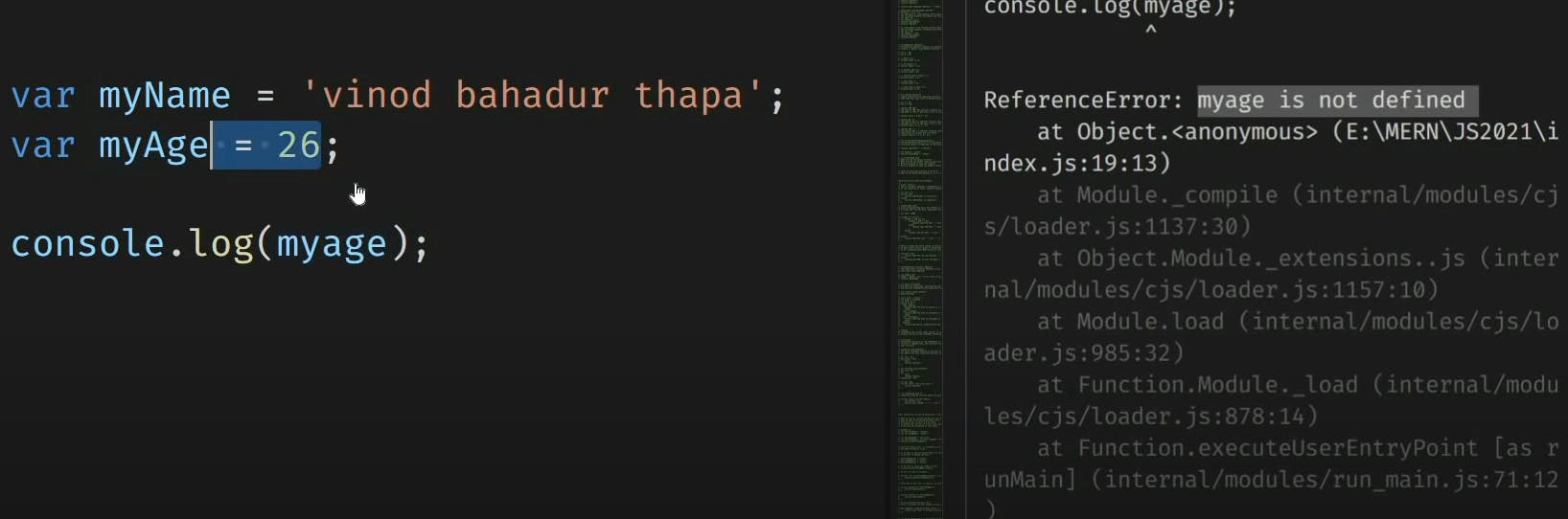
➡️The first character must be a letter or an underscore ( - ) or an dollar ( $ . You can't use a number as the first character .
➡️The rest of the variable name can include any letter , any number , or the underscore . Can use any other characters , but not spaces .
➡️ Variable names are case sensitive . No limit to the length of the variable name .
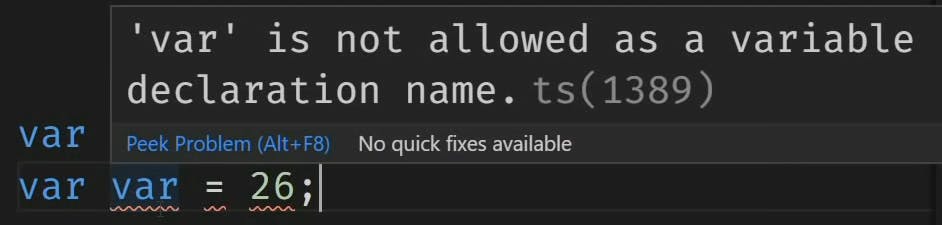
➡️You can't use any of JavaScript's reserved words as a variable name
➡️we cant use special character as name
📌What is Hoisting
Hoisting is JavaScript's default behaviour of moving declarations to the top.
Hoisting is a JavaScript mechanism where variables, function declarations and classes are moved to the top of their scope before code execution. Remember that JavaScript only hoists declarations, not initialisation. Let's take a simple example of variable hoisting,
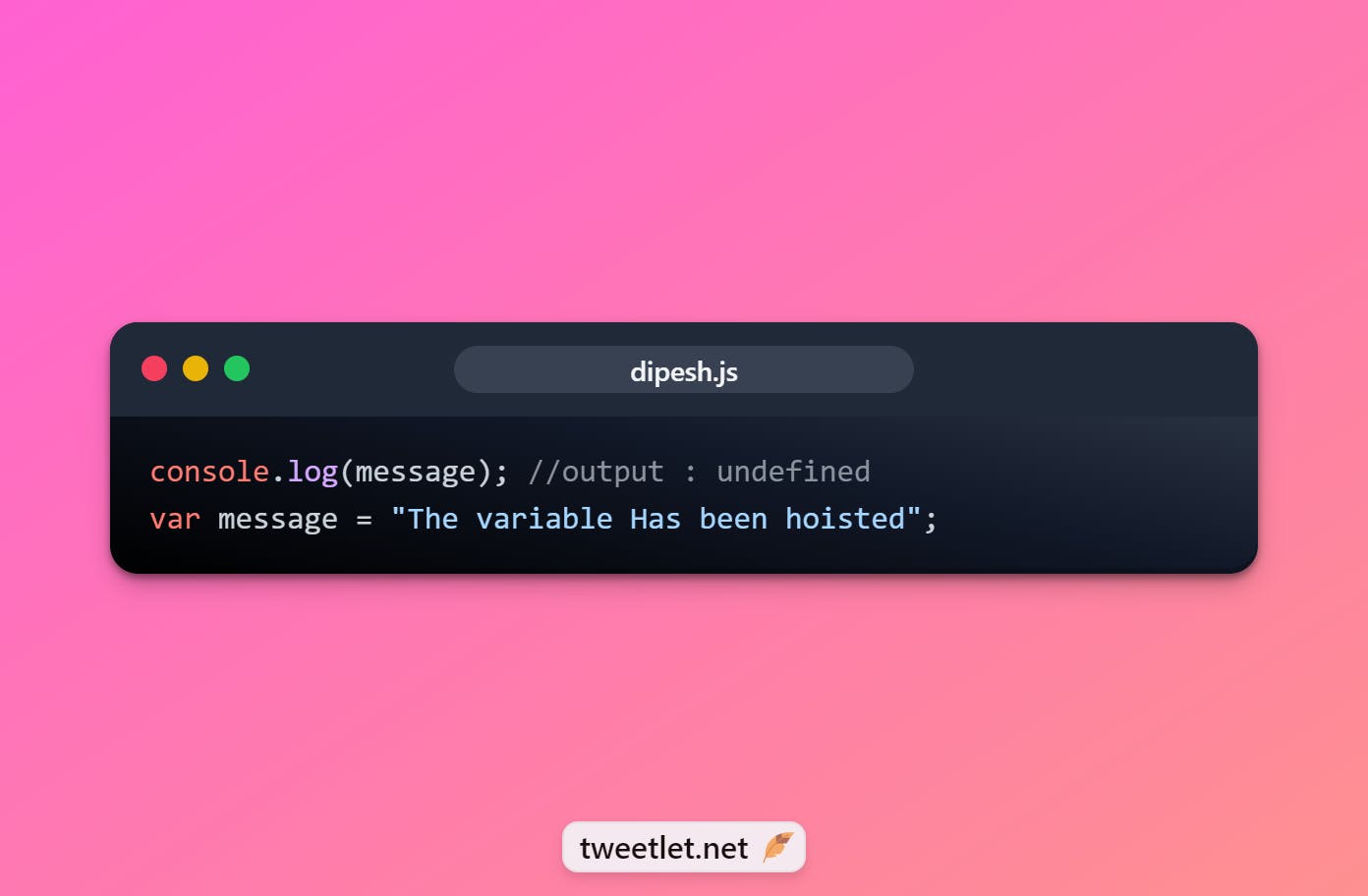
console.log(message); //output : undefined var message = "The variable Has been hoisted";
The above code looks like as below to the interpreter.
var message;
console.log(message);
message = "The variable Has been hoisted";
In the same fashion, function declarations are hoisted too
message("Good morning"); //Good morning function message(name) { console.log(name); }
This hoisting makes functions to be safely used in code before they are declared.
📌Variable Scopes
🪢Block Scopes
🪢Function Scopes
🪢 Global Scopes
📌BLOCK SCOPE
as per name block scope means the Variable value is only limit in that block scope
🪢let
it is a block scope => {...............} the code betwween curly brackets
if (true) { age = 25; console.log(age); //answer get 25 } console.log(age); //error
🪢const
it is a block scope =>{...............} the code between curly brackets
if (true) {
const age = 25;
console.log(age); //answer get 25
}
console.log(age); //error
📌Function Scope
- var
➡️ It is a function scope
function years() { var age = 25; } console.log(age); //error => age is not definedif ‘var ‘ is in the function then it can't get outside function
if it's any other blocks then it gets the output
if (true) {
var age = 25;
console.log(age); //answer get 25
}
console.log(age); //25
- if variables we create and we can store any kind of data string, object, numeric value, array function
📌Global Scope
if age variabel value is 25 in the function then it can run in that only
if its outside function and simply alone in the file then its global scope. then alone value will be given as answer
while its is normal scope
var age = 32; if (true) { var age = 25; console.log(age); //answer get 25 } console.log(age); //answer get 25while it is in function
var age = 32;
function xyz()
{
var age = 25;
console.log(age); //answer get 25
}
xyz();
console.log(age); //answer get 32
📌Datatypes in Javascript
Six Data Types that are primitives
Boolean : typeof instance === " boolean "
undefined : typeof instance === " undefined "
Number : typeof instance === " number "
String : typeof instance === " string "
BigInt : typeof instance === " bigint "
Symbol : typeof instance === " symbol "
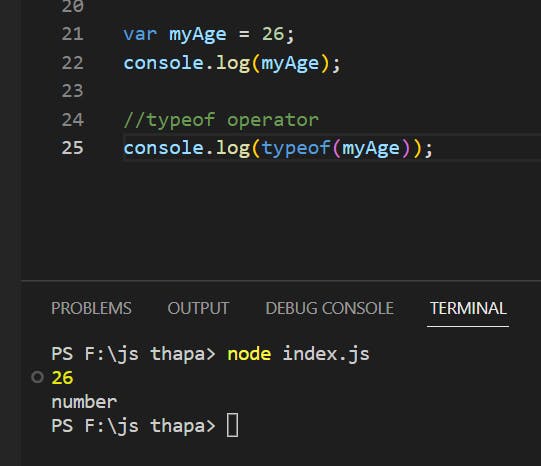
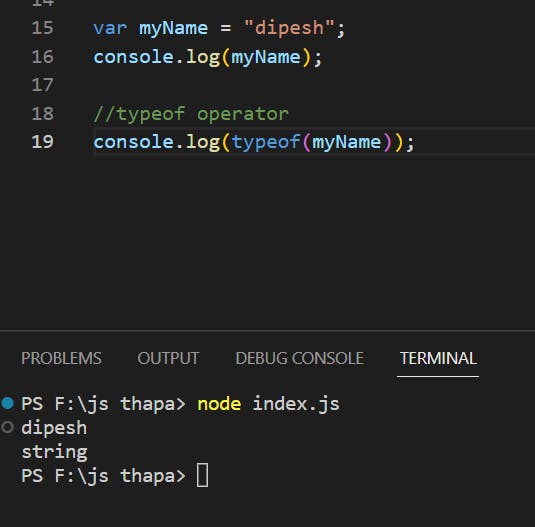
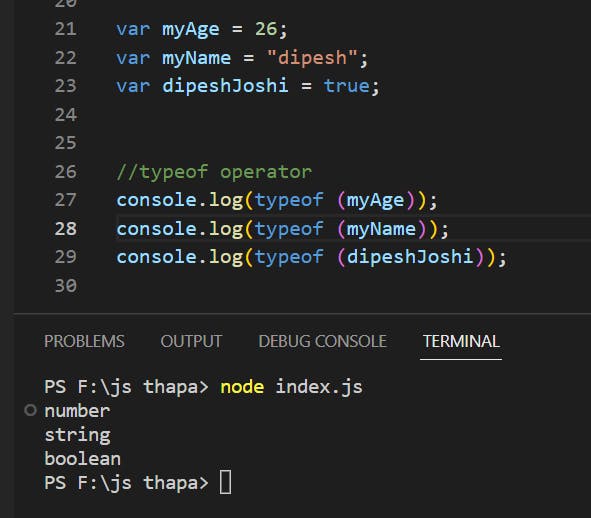
Example(Practise)
//10 + "20" // number + string so here 1020
//9 - "5" // number - string so here = 4 but its a bug
//"Java" + "Script" //string + string = concate and its javascript
//" " + " " //empty
//" " + 0 //0
//"vinod" - " thapa " //NaN = not a number
//js is
// true = 1
// false = 0
// true + true bool+bool = 1+1 = 2
// true + false bool+bool = 1+0 = 1
// false + true bool-bool = 0+1 = 1
// false - true bool-bool = 0-1 = 1
IQ: DIFFERENCE BETWEEN NULL VS UNDEFINED
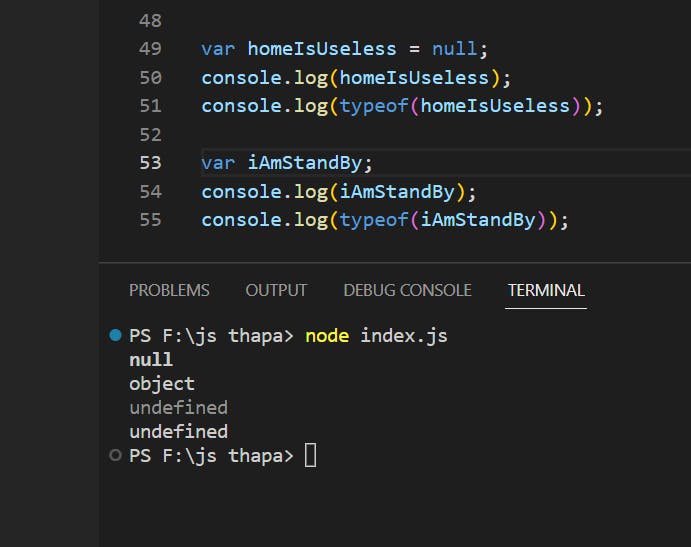
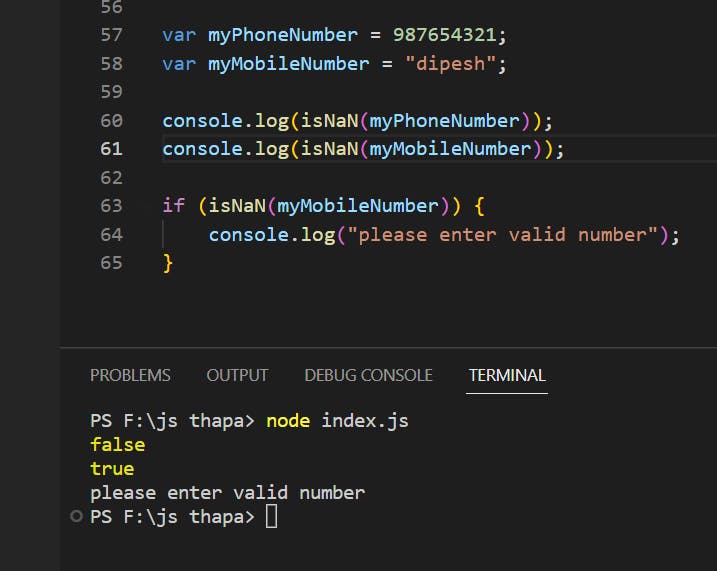
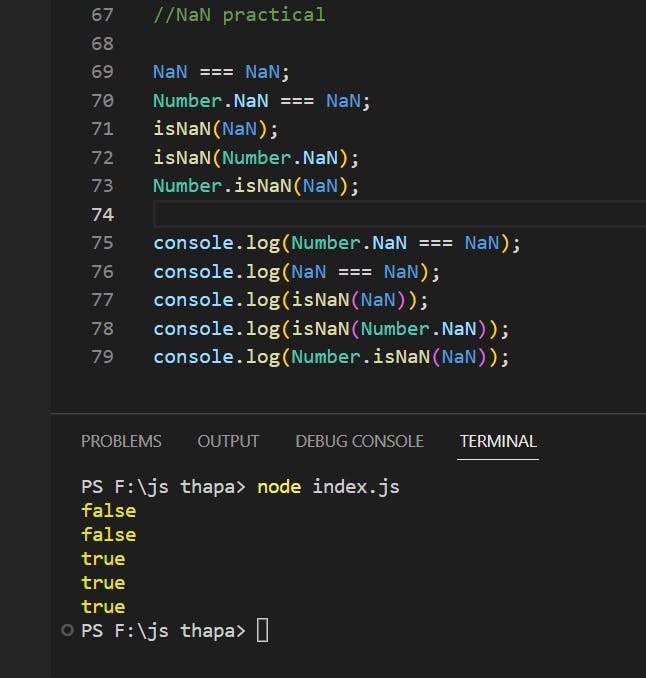
IQ: WHAT IS NaN?
console.log(”dipesh” - “joshi”) // NaN
NaN is a property of the global object .
In other words , it is a variable in global scope .
The initial value of NaN is Not - A - Number
Example(Practise)
Expression And Operators
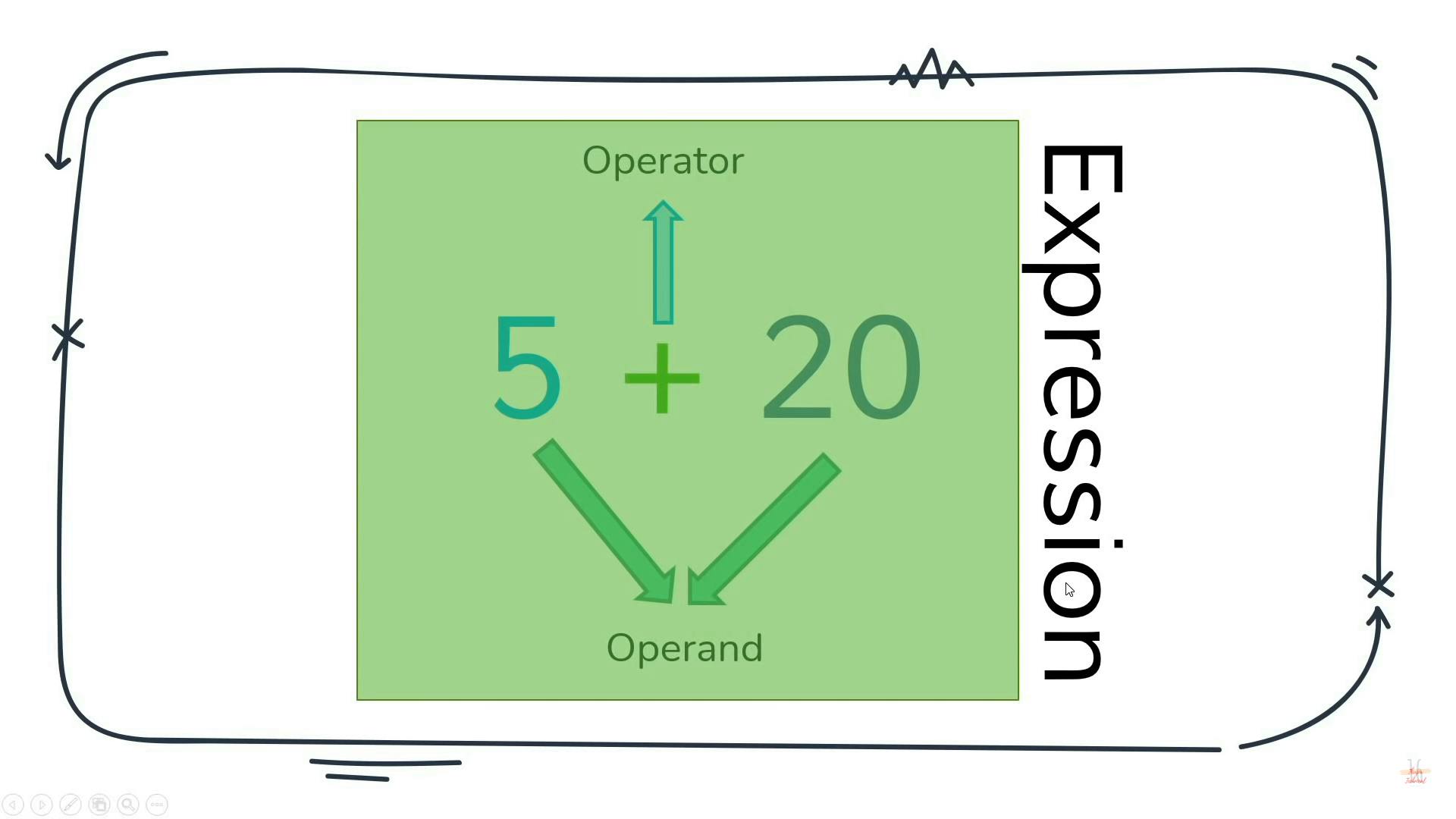
1 Assignment operators
- An assignment operator assigns a value to its left operand based on the value of its right operand .
The simple assignment operator is equal ( = )
var x = 5 ; var y = 5 ;
I will tell you when we will see es6 console.log
( Is both the x and y are equal : $ { x || = y } ) ;
2 Arithmetic operators
- An arithmetic operator takes numerical values ( either literals or variables ) as their operands and returns a single numerical value .
console.log ( 3 + 3 ) ;
console.log ( 10-5 ) ;
console.log ( 20/5 ) ; |
console.log ( 5 * 6 ) ;
- the modulus operator(%)returns the division remainder
console.log ( " Remainder Operator " + 81 % 8 ) ;
Increment and Decrement operator
Operator : x++ x-- or ++x --x
- If used postfix , with operator after operand ( for example , x ++ ) ,
the increment operator increments and returns the value before incrementing .
- If used prefix , with operator before operand ( for example , + x ) ,
the increment operator increments and returns the value after incrementing
3 Logical operators
Logical operators are typically used with Boolean ( logical ) values ; when they are , they return a Boolean value .
var a = 30 ; var b = -20 ; Logical AND ( && ) The logical AND ( && ) operator ( logical conjunction ) for a set of operands is true if and only if all of its operands are true . Logical OR ( || ) The logical OR ( || ) operator ( logical disconjunction ) for a set of operands is true if and only if one or more of its operands is true . Logical NoT (!) the logical not(!) operator (logical complement,negattion) takes truth to falsity and vice versa4 Comparison operators
var a = 30 ; var b = 10 ; // Equal ( == ) console.log ( a == b ) ; // Not equal ( != ) console.log ( a != b ) ; // Greater than ( > ) console.log ( a > b ) ; // Greater than or equal ( >= ) console.log ( a >= b ) ; // Less than (<) console.log ( a <= b ) ; // Less than or equal (<=) console.log(a <= b);
5 String Concatenation(operators)
- The concatenation operator (+) concatenates two string values together, returning another string that is the union of the two operand strings
Example(Practise)
//Exponentiation Operator
// What will be the output of 3**3?
// console.log(3**3); //27
// console.log(3**5); // 3*3*3*3*3 =243
//console.log(10 ** -1); // 1/10 =0.1
// What will be the output, when we add a number and a string ?
// console.log(5 + "thapa"); //5thapa
// console.log(5 - "thapa"); //NaN
// Write a program to swap two numbers?
var a = 5;
var b = 10;
//output b=5 and a=10
var c = b; //c=10
b = a; //b = 5
a = c;
console.log("the value of a is " + a);
console.log("the value of b is " + b);
// Write a program to swap two numbers without using third variable
var a = 5;
var b = 10;
//output b=5 and a=10
a = a + b; //a = 15
b = a - b; //b = 5
a = a - b; //a = 10
console.log("the value of a is " + a);
console.log("the value of b is " + b);
IQ: WHAT IS the difference between == vs ===?
\== check only value === check value and its datatype